SN74GTL2006PWR
Manufacturer No:
SN74GTL2006PWR
Manufacturer:
Description:
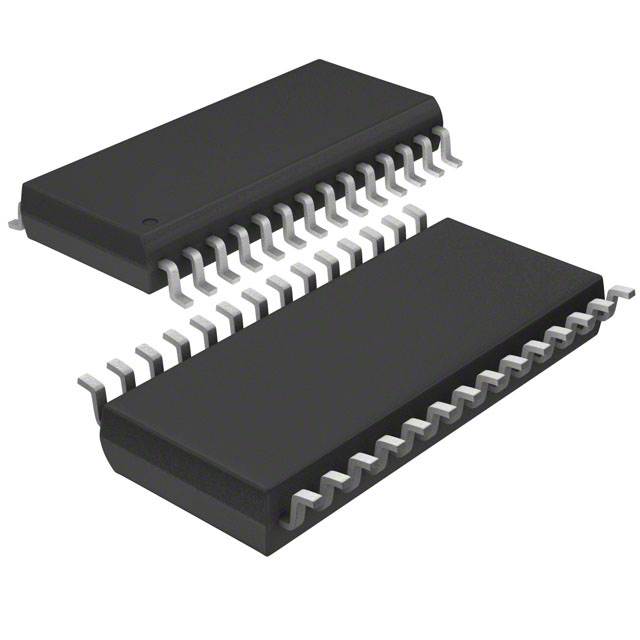
IC TRANSLATOR UNIDIR 28TSSOP
Datasheet:
Delivery:





Payment:




In Stock : 0
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.









SN74GTL2006PWR Specifications
-
TypeParameter
-
Supplier Device Package28-TSSOP
-
Package / Case28-TSSOP (0.173", 4.40mm Width)
-
Mounting TypeSurface Mount
-
Features-
-
Operating Temperature-40°C ~ 85°C (TA)
-
Data Rate-
-
Output TypeOpen Drain
-
Output SignalLVTTL
-
Input SignalGTL
-
Channels per Circuit13
-
Number of Circuits1
-
Channel TypeUnidirectional
-
Translator TypeMixed Signal
-
PackagingCut Tape (CT)
-
PackagingTape & Reel (TR)
-
Product StatusActive
-
Series74GTL
The SN74LVC4245APWT is a voltage-level translator and bus transceiver integrated circuit chip manufactured by Texas Instruments. It offers various advantages and is suitable for several application scenarios:Advantages: 1. Voltage-level translation: The SN74LVC4245APWT can translate signals between different voltage domains, making it suitable for interfacing devices operating at different voltage levels. 2. Bidirectional communication: It supports bidirectional communication, facilitating data transmission in both directions on a bus. 3. High-speed operation: The chip operates at high speeds, allowing for quick data transfer. 4. Low power consumption: It is designed to consume low power, making it suitable for battery-powered devices. 5. Multiple output-enable controls: The chip features individual output-enable controls for each direction, providing flexibility in data flow control.Application scenarios: 1. Interfacing between different voltage domains: The SN74LVC4245APWT can be used to interface components operating at different voltage levels. For example, it can be used to connect a microcontroller operating at 3.3V to a sensor operating at 5V. 2. Bus communication: The chip is commonly used to enable communication between microcontrollers or other devices on a shared bus, such as I2C or SPI. 3. Level shifting: It can be employed to shift the voltage levels of digital signals, facilitating data exchange between incompatible systems. 4. Mixed-voltage system integration: The chip is suitable for integrating subsystems or modules operating at different voltage levels into a single system. 5. Battery-powered devices: Its low power consumption makes it an excellent choice for applications where power efficiency is critical, particularly in battery-operated devices.It is important to note that the mentioned advantages and application scenarios are generic and may vary depending on specific system requirements and use cases.
SN74GTL2006PWR Relevant information
-
NL3X5004MU2TAG
onsemi -
NL3X5004DR2G
onsemi -
NL3X5004DTR2G
onsemi -
V62/22604-01XE
Texas Instruments -
NCA9701GXX
Nexperia USA Inc. -
MAX14591ETA+
Analog Devices Inc./Maxim Integrated -
SN74AVCA164245DGG
Texas Instruments -
74AVC1T45DBVR
Texas Instruments -
74AVC1T45DEAR
Texas Instruments -

SN74LVC1T45DCKR-P
Texas Instruments