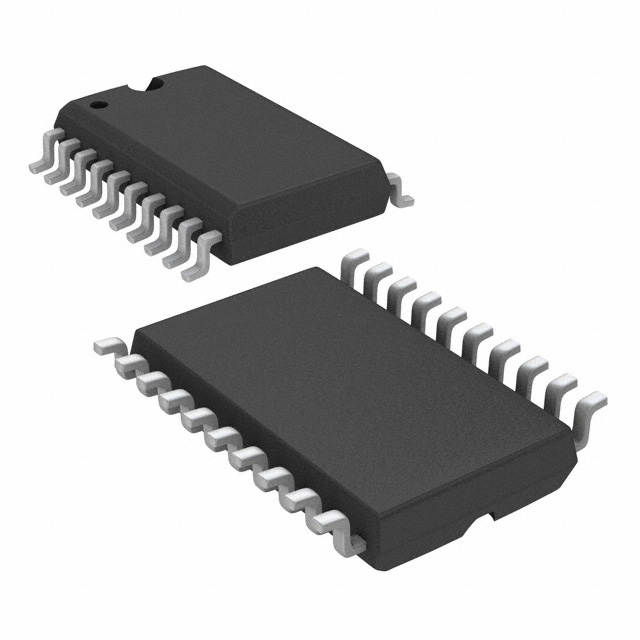
SN74BCT29821DWR
Manufacturer No:
SN74BCT29821DWR
Manufacturer:
Description:
IC FF D-TYPE SNGL 10BIT 20SOIC
Datasheet:
Delivery:





Payment:




In Stock : 0
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.









SN74BCT29821DWR Specifications
-
TypeParameter
-
Input Capacitance5.5 pF
-
Clock Frequency125 MHz
-
Package / Case24-SOIC (0.295", 7.50mm Width)
-
Supplier Device Package24-SOIC
-
Mounting TypeSurface Mount
-
Operating Temperature0°C ~ 70°C (TA)
-
Current - Quiescent (Iq)10 mA
-
Voltage - Supply4.5V ~ 5.5V
-
Current - Output High, Low24mA, 48mA
-
Trigger TypePositive Edge
-
Max Propagation Delay @ V, Max CL10ns @ 5V, 50pF
-
Number of Bits per Element10
-
Number of Elements1
-
Output TypeTri-State, Non-Inverted
-
TypeD-Type
-
FunctionStandard
-
PackagingTape & Reel (TR)
-
Product StatusObsolete
-
Series74BCT
The SN74BCT29821DWR is a specific type of integrated circuit chip that belongs to the SN74BCT series of devices. It is a 9-bit universal shift/storage register with 3-state outputs. Here are some advantages and application scenarios of this chip:Advantages: 1. Versatility: The SN74BCT29821DWR chip can be used as a shift register or a storage register, providing flexibility in various applications. 2. High-speed operation: It operates at high clock frequencies, making it suitable for applications that require fast data transfer. 3. 3-state outputs: The chip has 3-state outputs, which means it can be easily connected to a bus system without causing any conflicts or bus contention issues. 4. Wide operating voltage range: It can operate within a wide voltage range, typically from 4.5V to 5.5V, allowing compatibility with different power supply systems.Application scenarios: 1. Serial data transfer: The chip can be used in applications where serial data needs to be shifted in or out, such as serial communication protocols or data storage systems. 2. Parallel-to-serial conversion: It can be used to convert parallel data into serial data for transmission over a single line, commonly used in serial communication interfaces like UART or SPI. 3. Data storage: The chip can store data in its internal registers until it is needed, making it suitable for applications that require temporary data storage or buffering. 4. Bus systems: The 3-state outputs of the chip make it ideal for connecting to bus systems, such as address or data buses in microprocessors or digital systems, where multiple devices need to share the same bus.It's important to note that the specific advantages and application scenarios may vary depending on the overall system requirements and the specific use case.
SN74BCT29821DWR Relevant information