In Stock : 0
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.









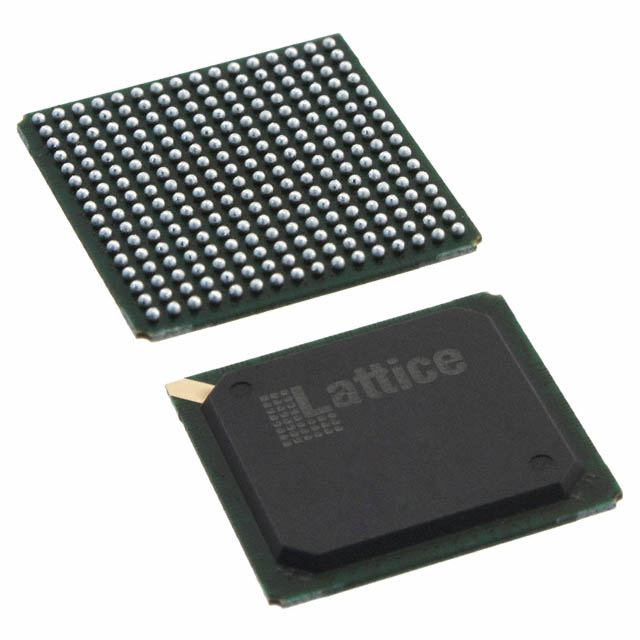
1SG110HN1F43I1VG Specifications
-
TypeParameter
-
Supplier Device Package1760-FBGA (42.5x42.5)
-
Package / Case1760-BBGA, FCBGA
-
Operating Temperature-40°C ~ 100°C (TJ)
-
Mounting TypeSurface Mount
-
Voltage - Supply0.77V ~ 0.97V
-
Number of I/O688
-
Number of Logic Elements/Cells1100000
-
Number of LABs/CLBs137500
-
DigiKey ProgrammableNot Verified
-
PackagingTray
-
Product StatusActive
-
SeriesStratix® 10 GX
The 1SG110HN1F43I1VG integrated circuit chips, also known as FPGAs (Field-Programmable Gate Arrays), have several advantages and application scenarios:Advantages: 1. Flexibility: FPGAs can be reprogrammed or reconfigured to perform different functions, making them highly flexible compared to fixed-function ASICs (Application-Specific Integrated Circuits). 2. High performance: FPGAs can achieve high processing speeds and parallelism, making them suitable for applications that require real-time processing or high-performance computing. 3. Customizability: FPGAs allow designers to create custom logic circuits tailored to specific applications, enabling optimization for performance, power consumption, or other requirements. 4. Prototyping and development: FPGAs are commonly used for prototyping and development of complex digital systems, as they provide a platform for testing and refining designs before committing to ASIC production. 5. Cost-effective: FPGAs can be more cost-effective than ASICs for low to medium volume production runs, as they eliminate the need for expensive mask sets and reduce development time.Application Scenarios: 1. Communications and networking: FPGAs are used in routers, switches, and network infrastructure equipment to handle high-speed data processing, packet routing, and protocol conversion. 2. Signal processing: FPGAs are employed in applications such as digital signal processing (DSP), image and video processing, audio processing, and software-defined radio (SDR). 3. Industrial automation: FPGAs are utilized in industrial control systems, robotics, and automation equipment for real-time control, sensor interfacing, and data acquisition. 4. Aerospace and defense: FPGAs are used in radar systems, avionics, satellite communication, and military applications for their high-performance computing capabilities and ability to withstand harsh environments. 5. Automotive: FPGAs find applications in advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), infotainment systems, engine control units (ECUs), and in-vehicle networking for processing sensor data, image recognition, and connectivity. 6. Internet of Things (IoT): FPGAs can be integrated into IoT devices for edge computing, sensor data processing, and connectivity, enabling real-time analytics and decision-making at the device level.These are just a few examples, and the versatility of FPGAs allows them to be used in various other domains where programmable logic and high-performance computing are required.