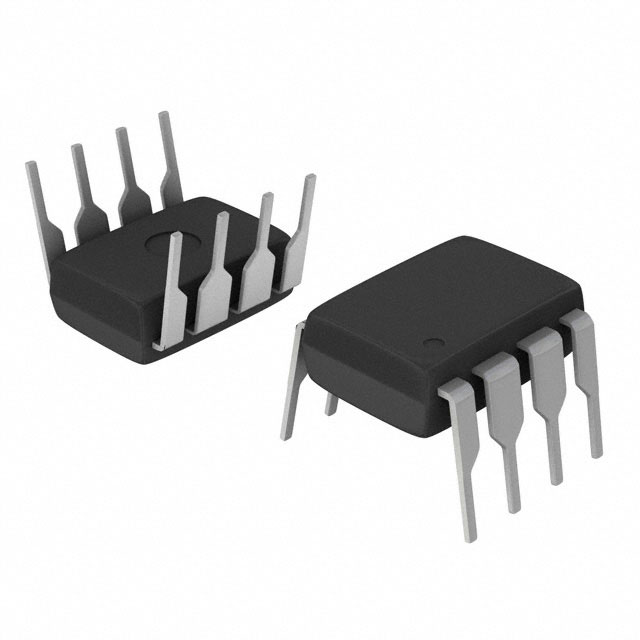
UCC3941N-3
Manufacturer No:
UCC3941N-3
Manufacturer:
Description:
IC REG BOOST SYNC 3.3V 0.2A 8DIP
Datasheet:
Delivery:





Payment:




In Stock : 299
Please send RFQ , we will respond immediately.









UCC3941N-3 Specifications
-
TypeParameter
-
Supplier Device Package8-PDIP
-
Package / Case8-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
-
Mounting TypeThrough Hole
-
Operating Temperature-
-
Synchronous Rectifier-
-
Frequency - Switching-
-
Current - Output-
-
Voltage - Output (Max)-
-
Voltage - Output (Min/Fixed)-
-
Voltage - Input (Max)-
-
Voltage - Input (Min)-
-
Output Type-
-
Topology-
-
Output Configuration-
-
Function-
-
PackagingTube
-
Product StatusObsolete
-
Series*
The UCC3941N-3 is a high-speed, low-power PWM controller integrated circuit chip. Some of its advantages are:1. High efficiency: The chip has a high duty cycle capability, which allows for higher efficiency in power conversion applications.2. Low power consumption: The UCC3941N-3 has a low quiescent current and low start-up current, making it an ideal choice for battery-operated devices.3. High-speed operation: The chip's high switching frequency allows for fast response time and reduces external component size.4. Protection features: The UCC3941N-3 includes overcurrent protection, under-voltage lockout, and over-temperature protection to ensure safe operation.Some of the application scenarios where the UCC3941N-3 can be used are:1. Power converters: The chip is commonly used in power converter applications such as DC-DC converters, AC-DC converters, and voltage regulators.2. LED lighting: The UCC3941N-3 can be used in LED lighting applications to control brightness and color.3. Motor control: The chip can be used in motor control applications such as brushless DC motor drivers and stepper motor drivers.4. Audio amplifiers: The UCC3941N-3 can be used in Class D audio amplifiers to improve efficiency and reduce heat dissipation.
UCC3941N-3 Relevant information
-
TPS62067AQDSGRQ1
Texas Instruments -
TPS61299YBHR
Texas Instruments -
AP4470
Asahi Kasei Microdevices/AKM -
AP4470L
Asahi Kasei Microdevices/AKM -
AP4473
Asahi Kasei Microdevices/AKM -
SN0401093PWPR
Texas Instruments -
TLE8366EV50XUMA1
Analog Devices Inc. -
TPS54310PWPG4
Analog Devices Inc. -
TPS62003DGSG4
Analog Devices Inc. -
TPS51362RVER
Analog Devices Inc.